
Batteries in series vs parallel series#
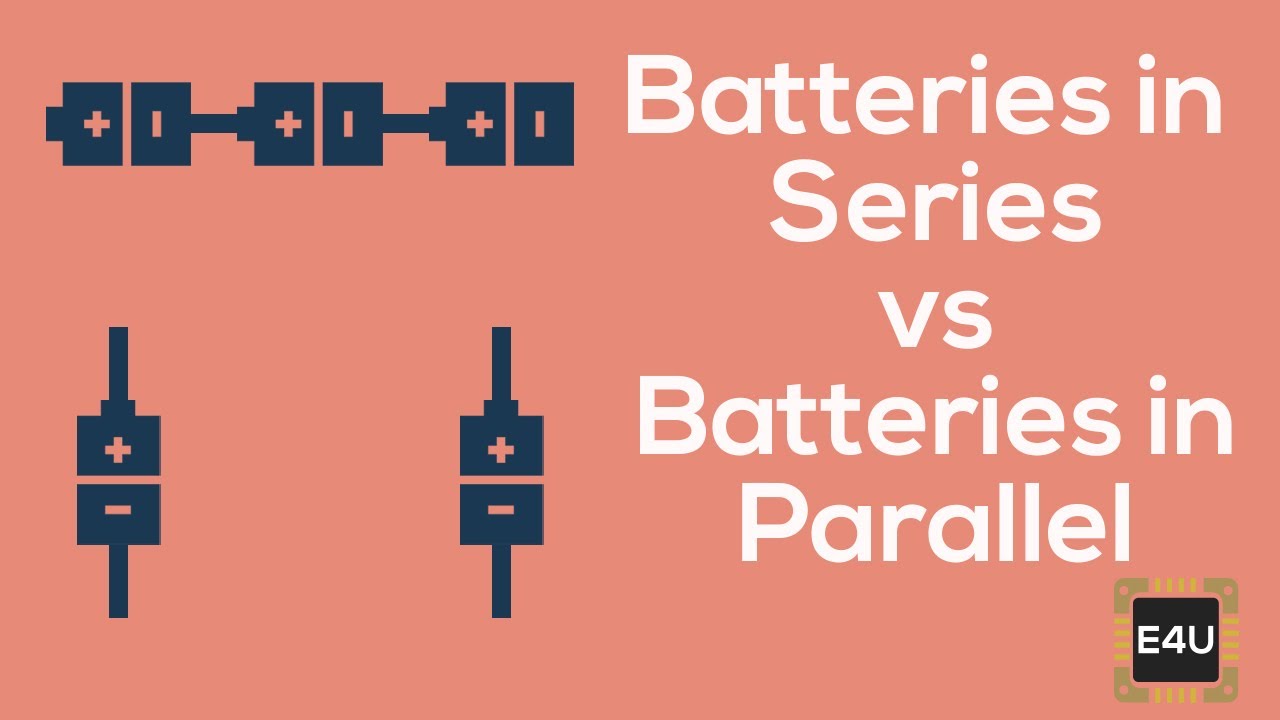
The current delivered by the battery is sum of currents delivered by individual cells.This guide will look at Series and Parallel Circuits and the benefits and downsides associated with each. The resultant internal resistance of the combination is, If emf of each cell is identical, then the emf of the battery combined by n numbers of cells connected in parallel, is equal to the emf of each cell. These combinations are also referred as parallel batteries. When positive terminals of all cells are connected together and similarly negative terminals of these cells are connected together in a battery, then the cells are said to be connected in parallel. Similarly, if r 1, r 2, r 3, …………… r n are the internal resistances of individual cells, then the internal resistance of the battery will be equal to the sum of the internal resistance of the individual cells i.e. If E is the overall emf of the battery combined by n number cells and E 1, E 2, E 3, …………… E n are the emfs of individual cells. But overall discharged current of the battery does not exceed the discharged current of individual cells. Here, overall emf of the battery is algebraic sum of all individual cells connected in series. When in a battery, positive terminal of one cell is connected with the negative terminal of succeeding cell, then the cells are said to be series connected or simply series battery. Series Parallel Batteriesīattery cells can be connected in series, in parallel and as well as a mixture of both the series and parallel. The entire resistance encountered by a current as if it flows through a battery from the negative terminal to the positive terminal is known as internal resistance of battery.


If E is the emf or no-load voltage of the battery and V is the terminal voltage of load voltage of the battery, then E – V = internal voltage drop of the battery.Īs per Ohm’s law, this internal voltage drop is nothing but the product of electrical resistance offered by the battery and the current flows through it.
terminal voltage of battery when load is connected, he or she will get the voltage which is less than emf of the battery by internal voltage drop of the battery. So, if any one measures the terminal voltage of the load i.e. Because of this internal resistance of battery, there will be some voltage drops across it. As a battery is an electrical equipment, it must have some electrical resistance inside it. Actually when load is connected with the battery, there will be load current flowing through it. Terminal voltage of battery is the potential difference across its terminals when the current is being drawn from it. It is also referred as no-load voltage of battery. This voltage is generally referred as electromotive force or emf of battery. If anyone just measures the electric potential difference between two terminals of a battery when load is not connected with the battery, he or she will get the voltage developed in the battery when there is no current flowing through it. So a 12 volt battery will have total 6 number of cells connected in series. For example, Nickel-cadmium battery cells normally develop about 1.2 V per cell while lead acid battery develop about 2 V per cell. Hence it can be concluded like that, a battery is a combination of several cells where a cell is a unit of a battery. For achieving desired electric potential difference across the battery terminals multiple numbers of cells are to be connected in series. Every electrochemical reaction has its limit of producing electric potential difference between two electrodes.īattery cells are those where these electro-chemical reactions take place to produce the limited electric potential difference. Battery is an electrical element where electrical potential is produced due to chemical reaction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
